Controlling the Size of the Windows Page File
The Windows page file is a system file stored on your disk drive at C:\pagefile.sys. The page file is used to allow virtual memory to work correctly. (Understanding virtual memory is covered under another tip.) This file is typically sized to the amount of physical memory in your computer. So, if you have 16 GB of memory in your system, the size of the page file will also be 16 GB. Windows controls this file, so it is recommended that you leave it alone.
If, for some reason, you want to control the size of the page file yourself, how you start depends on the version of Windows you are using. If you are using Windows 7, click the Start button, right-click Computer, and select Properties. A Control Panel screen appears that displays some information about your system.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 10, you display the same screen by displaying the Control Panel, clicking on the System and Security link, and then clicking the System link.
Regardless of the version of Windows you are using, you should now follow these steps:
- At the left side of the screen click Advanced System Settings. Windows displays the System Properties dialog box; the Advanced tab should be displayed. (See Figure 1.)
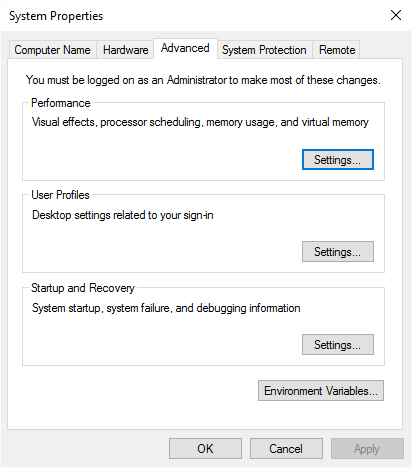
Figure 1. The Advanced tab of the System Properties dialog box.
- In the Performance area of the dialog box, click the Settings button. (This is the first of three Settings buttons in the dialog box.) Windows displays the Performance Options dialog box.
- Make sure the Advanced tab is displayed. (See Figure 2.)
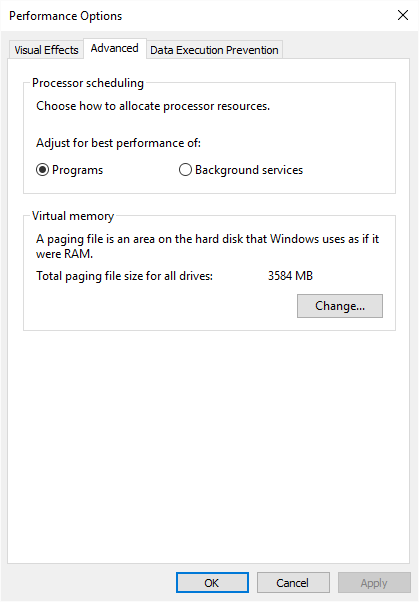
Figure 2. The Advanced tab of the Performance Options dialog box.
- Click the Change button. Windows displays the Virtual Memory dialog box. (See Figure 3.)
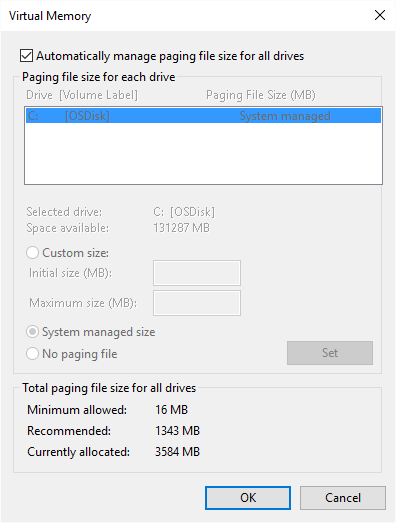
Figure 3. The Virtual memory dialog box.
- Clear the first check box on the dialog box. (The one that specifies Windows automatically managers the paging file size.)
- In the list of drives on your system, select the drive where you want a paging file located.
- Click the Custom Size radio button.
- Specify an Initial Size and Maximum Size setting, in megabytes, for the paging file.
- Click Set.
- Repeat steps 6 through 9 for each drive on which you want a paging file.
- Click OK and close all other open dialog boxes.
- Restart your system.
Author Bio
Barry Dysert
Barry has been a computer professional for over 35 years, working in different positions such as technical team leader, project manager, and software developer. He is currently a software engineer with an emphasis on developing custom applications under Microsoft Windows. When not working with Windows or writing Tips, Barry is an amateur writer. His first non-fiction book is titled "A Chronological Commentary of Revelation." Learn more about Barry...
How to Run a Program when Windows Starts
It's easy to have a program run when Windows starts. In fact, by using the Task Scheduler, you can have all sorts of ...
Discover More
Changing User Permissions for an Entire Drive
All objects on your computer (e.g., disk drives) have permissions that allow or deny various types of access. This tip ...
Discover More
Stopping Windows from Creating Thumbs.db Files
Many times, the automatically created Thumbs.db file is more trouble than it's worth. If you want to stop Windows from ...
Discover More
Creating a System Repair Disc
Doing a one-time create of a system repair disk can be worth its weight in gold if you find yourself unable to boot your ...
Discover More
Repairing Your System Using a System Repair Disk
If your system gets into a state where it cannot be started normally, this tip presents you with options of how you can ...
Discover More
Getting Information about Files Searched For
Do a search for files on your computer and you may need to see more information about the results than what Windows first ...
Discover More



![]()
![]()
![]() This tip (12629) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
This tip (12629) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
Comments