There are several types of event logs maintained by the Windows operating system. One of these is the Application event log. This log is used to record events written by applications and services. The applications may be commercial applications, like SQL Server or Exchange, or they may be custom applications that you've developed yourself. The events written to the Application event log can run the gamut from application startup events to shutdown events to "heartbeat" events to run-time error events. The same holds true for events written by Windows services.
Like events written to other event logs, some of the important elements written to the Application log include the date and time when the event occurred, the event ID, and the event source. (See Figure 1.)
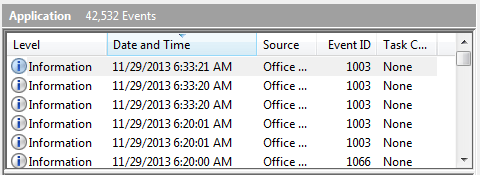
Figure 1. Partial display of the Application event log.
Events can be viewed by using the Event Viewer. By default they are presented in reverse chronological order (i.e., the most recent event is on top). You can, however, sort the events by any of the event columns by clicking the column header.
![]()
![]()
![]() This tip (12886) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
This tip (12886) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
The Forwarded Events event log collects events that have been forwarded from other computers. In this way you can login ...
Discover MoreEvent logs are used to store information about what goes on, behind the scenes, on your system. Whether you want to ...
Discover MoreBy default, the event logs are implemented in a circular buffer, i.e., when its maximum size is reached, the oldest ...
Discover MoreThere are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Copyright © 2025 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments