Changing How Event Log Overruns are Handled
The system's event logs don't grow forever. By default, when they hit their maximum allowable size Windows deletes the oldest log file entries and continue to write new ones. You can change this default behavior if you wish.
For example, let's say that I want to change how the System event log's overruns are handled. I can do so by following these steps:
- Display the Event Viewer. (The easiest way to do this is to use the search capabilities of Windows to look for "Event Viewer", without the quote marks.)
- In the Navigation pane (left side of the Event Viewer), expand the Windows Logs node and click on System.
- In the right pane, click Properties. Windows displays the Log Properties dialog box for the System event log. (See Figure 1.)
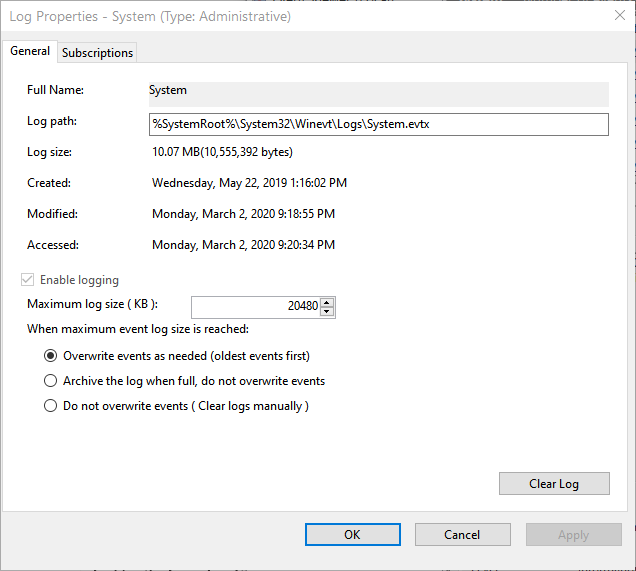
Figure 1. Changing how log overruns are handled.
- Using the three radio buttons at the bottom of the dialog box, specify what you want to happen when the maximum log file size is reached.
- Click OK.
The three options for handling large log files may need a bit of explaining. Windows provides these options:
- Overwrite Events as Needed. This is the default behavior, i.e., the oldest events are deleted to make room for the new events.
- Archive the Log when Full. The event log is automatically archived and a new one is created. No events are lost. This is a good choice if you think that there may be some events occur on your system which result in a rapid escalation in the number of events being logged.
- Do Not Overwrite Events. The event log is cleared, and new ones get written to the empty log file. It is unclear how this choice could ever be desirable, but there you have it.
Author Bio
Barry Dysert
Barry has been a computer professional for over 35 years, working in different positions such as technical team leader, project manager, and software developer. He is currently a software engineer with an emphasis on developing custom applications under Microsoft Windows. When not working with Windows or writing Tips, Barry is an amateur writer. His first non-fiction book is titled "A Chronological Commentary of Revelation." Learn more about Barry...
How to Remove Cortana's Search Box
If you want to free up some space on the taskbar, consider eliminating Cortana's search box. This tip tells you how.
Discover More
Rebuilding the Search Index
There may be times when you want to reset the search index and rebuild it from scratch. This tip tells you how.
Discover More
Renaming Files Using the Command Line
The rename command can really be a timesaver over trying to do the similar sort of thing with Windows Explorer. You can ...
Discover More
Deleting Events in Your Event Logs
You don't need to worry about event logs filling up your disk, but you still may want to clean them out eventually. This ...
Discover More
Using the Event Viewer to Examine Remote Event Logs
Assuming you have proper access to remote computers, you can examine their event logs from your system without much ...
Discover More
What is the Purpose of the Application Event Log?
The Application event log holds messages generated by applications and services. This tip explains more about it.
Discover More

![]()
![]()
![]() This tip (12749) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
This tip (12749) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
Comments