Command Prompt is an extremely powerful tool that allows you to control your computer in various ways. One helpful way to use the Command Prompt is to get the contents of a folder. Often, we have a folder or directory that houses many additional directories and files. Getting a list of items in a directory can prove helpful. Obtaining a list of directory contents is a problem that a WindowsTips reader, Liz, had written about. She asked how one could do this without downloading a third-party app or messing with the Registry.
When it comes to this type of request, the first thing that comes to mind is using a PowerShell or Command Prompt tool, so this article focuses on using the latter, Command Prompt.
To start, press the Windows key, type (without quotes) "Command Prompt", and press Enter. This opens the Command Prompt window. Here you can use the Tree command to get a list of a directory's contents and add the list to a new text document. Do this by typing the following into the Command Prompt window:
tree "C:\Users\eric\Desktop\Main Directory" > "C:\Users\eric\Desktop\Main Directory\Contents.txt" /A /F
That's a long command, so make sure you type it all on one line. After you enter the command and press Enter, Windows creates a file titled "Contents.txt" in the location specified. That text file contains a listing of all the files and folders in the directory you specified. (See Figure 1.)
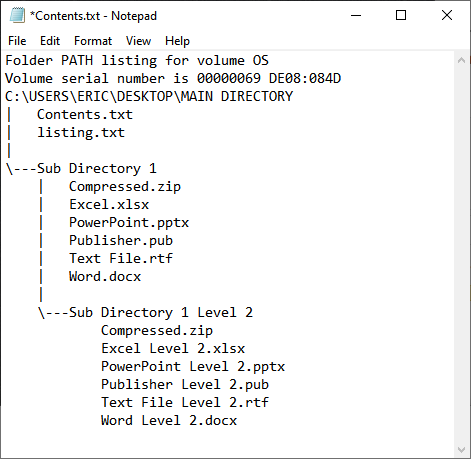
Figure 1. The names of items in a directory added into a .txt file.
To better understand the command, let's look at the parts we entered. There are four main parts. The first part of this command is the "Tree" command that we mentioned previously. The Tree command returns a graphical structure of the contents of a directory.
The second part, contained within the first set of quote marks, is the directory location from which you want Windows to gather information. A shortcut to obtain the directory location is to navigate in an Explorer window to the desired directory, click in the File Explorer location bar, copy the contents, and paste it in when needed in Command Prompt. (See Figure 2.)
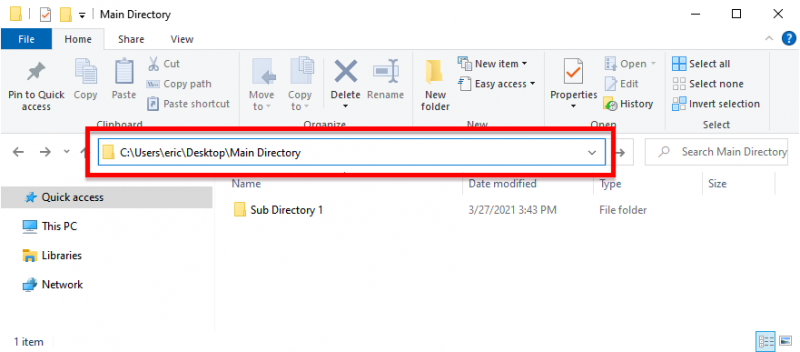
Figure 2. The location of a folder within the Explorer window.
The third part of the command is the ">" character; this passes the information from the first part to the last part of the command. In other words, the output of the first part is used as input for the last part.
The fourth part of the command is within the second set of quote marks. This indicates where Command Prompt will save the information—the location and name of the file in which to save the data. In this instance, we named the resulting file "Contents.txt", however, we just as easily could have called it "directory.txt" or "Results.txt". Directly following the location and file name are the "/A" and "/F" switches. When used with the Tree command, these switches tell Command Prompt to return the information in an ASCII format and to look through all subfolders recursively.
With this small command, it is easy to get and save the names of any items within any folder or directory and save that information into a text file for printing or other uses.
![]() This tip (13841) applies to Windows 10.
This tip (13841) applies to Windows 10.
The MOVE command can be a timesaver over trying to do the similar sort of thing with File Explorer. You can move hundreds ...
Discover MoreFinding data within files is a common need. If what you're looking for is in a flat file, you can find what you're after ...
Discover MoreIP addresses identify your device on IP-governed networks. If you need to find your IP address quickly, you can use the ...
Discover MoreThere are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments