Windows batch files are great if you want to perform several tasks in quick succession, or if you want to do things to several files in a row, or if you simply don't want to use the GUI interface to perform some tasks (e.g., performing unattended tasks). Batch files are text files with a ".bat" extension and contain Windows' command-line statements. Of course, you need to know the command-line statements in order to enter them into a .bat file. There are many places on the Web that describe the available command-line statements, but one place is the following:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754340.aspx#BKMK_Index
There are various ways to create a batch file, but since a batch file is nothing but a plain text file, perhaps the simplest way is to use Notepad. Since I use batch files a lot, I created a C:\Bat folder where I keep them all. To create a new one I use Windows Explorer or File Explorer to navigate to C:\Bat, then I right-click in that folder and select New | Text Document. (See Figure 1.)
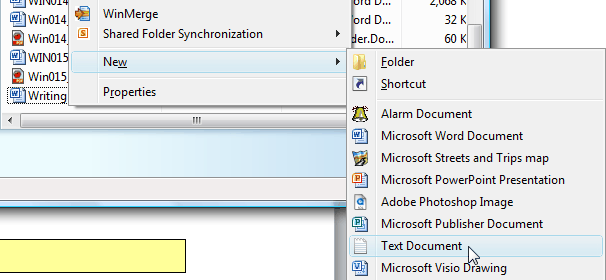
Figure 1. Creating a new text document.
Immediately after selecting the Text Document menu item, type the name you want to give to your batch file (say you want it to be called "Directory") and press Enter. Now, pressing Enter a second time will launch Notepad, and you can begin typing in the command-line statements that constitute your batch file.
For example, say you wanted to create a batch file that produces a directory listing of a folder, and puts that listing into a file named "Dirlist.txt". The command-line statement that produces a directory listing is DIR, and to direct DIR's output to a file you use the ">" operator. So the line you type into Notepad would be:
DIR > Dirlist.txt
Command-line statements are not case sensitive, so you don't need to type DIR in uppercase if you don't want to. After you've typed this into Notepad, save the file and exit. The last thing to do before actually invoking your batch file is to rename it to have a ".bat" extension instead of the default ".txt" extension. Here again, under Windows Explorer or File Explorer, right-click the file you just created ("Directory.txt") and select Rename from the Context menu. Use the right-arrow key to move over to the ".txt" portion of the file name and replace ".txt" with ".bat" and then press Enter. (Windows will ask you if you're sure you want to rename the file. Click Yes.) You should now have a file named "Directory.bat" in your folder.
One way to invoke a batch file is to double-click on it, so to actually execute your DIR command, double-click the "Directory.bat" file. Immediately, a window will briefly appear and disappear, and you'll now see a file named "Dirlist.txt" in your folder. This file was created by the commands in the batch file. By opening that file you'll see a directory listing of your C:\Bat folder.
Obviously, having a batch file that produces a directory listing of your C:\Bat folder is of limited value, but this tip was meant to give you an introduction to creating and invoking a simple batch file. But the batch processing capabilities are very powerful. See other tips to get a feel for using slightly more sophisticated batch files.
![]()
![]()
![]() This tip (13100) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
This tip (13100) applies to Windows 7, 8, and 10.
This tip is part of a series that shows you how to create and use Windows batch files. It introduces a few commands and ...
Discover MoreSometimes your batch file needs to accept an unknown number of parameters. This is easy to deal with if you know about ...
Discover MoreThis tip is part of a series that talks about Windows batch files. It introduces a few more commands and special ...
Discover MoreThere are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments