Changing the Hidden Attribute for a File
When you create a file in Windows, that file has certain attributes that are associated with it. Sometimes these attributes seem obvious—things like file size and file name come to mind. Other times the attributes are less obvious and more esoteric. Once such attribute controls whether the file is displayed, by default, in Explorer windows. It is called, appropriately enough, the Hidden attribute.
To change the hidden attribute, follow these steps:
- Display an Explorer window. (The easiest way is to press Win+E.)
- Navigate until you see the file you want to affect.
- Right-click on the file and choose Properties from the resulting Context menu. Windows displays the Properties dialog box; the General tab should be visible. (See Figure 1.)
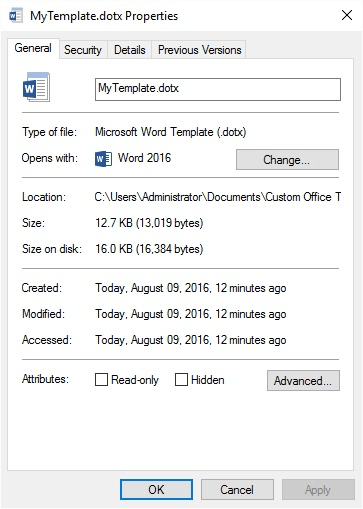
Figure 1. The Properties dialog box for a file.
- Use the Hidden checkbox (at the bottom of the dialog box) to specify whether the file should be hidden or not.
- Click OK.
When a file is hidden, it is not normally visible in the Explorer window. If you want to have hidden files included in what you see, follow these steps if you are using Windows 7 or Windows 10:
- Display the Control Panel by typing "Control Panel" (without the quotes) in the search box to the left of the task bar and press Enter if you are using Windows 10. If you are using Windows 7 click the Start menu and then click Control Panel.
- Click the Appearance and Personalization link.
- Click the Show Hidden Files and Folders link (under the File Explorer section). Windows displays the File Explorer Options dialog box. (See Figure 2.)
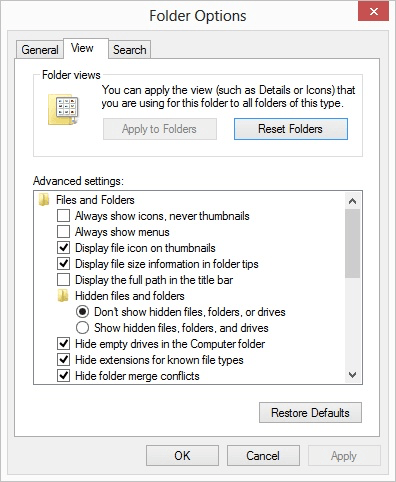
Figure 2. The File Explorer Options dialog box.
- Select the Show Hidden Files, Folders, and Drives radio button.
- Click OK.
With this setting made, all hidden files are displayed in all Explorer windows. If you are using Windows 10 you can also follow these steps:
- Press Win+E to display an Explorer window.
- At the top of the window, click the View tab.
- In the Show/Hide group (near the right side of the ribbon), make sure the Hidden Items check box is selected.

 This tip (13078) applies to Windows 7 and 10.
This tip (13078) applies to Windows 7 and 10.
Author Bio
Allen Wyatt
With more than 50 non-fiction books and numerous magazine articles to his credit, Allen Wyatt is an internationally recognized author. He is president of Sharon Parq Associates, a computer and publishing services company. Learn more about Allen...
Separating Grammar-Checking from Spell-Checking
Most of the time Word will check both grammar and spelling at the same time. You can, however, instruct the program to ...
Discover More
Evaluating Formulas
Need a bit of help in figuring out how Excel is evaluating a particular formula? It's easy to figure out if you use the ...
Discover More
Copying Form Field Contents
Are you developing a form with Word? In some instances it is advantageous to copy whatever is entered in a form field to ...
Discover More
Creating a Hierarchy Map of Your Hard Drive
Want to see how the directories and subdirectories in your hard drive are organized? It's easy to do using the directions ...
Discover More
Removing Temporary Files
Windows provides a workspace for programs to create temporary files, the Temporary folder. You can remove files from the ...
Discover More
Creating a System Repair Disc
Doing a one-time create of a system repair disk can be worth its weight in gold if you find yourself unable to boot your ...
Discover More


![]()
![]() This tip (13078) applies to Windows 7 and 10.
This tip (13078) applies to Windows 7 and 10.
Comments